
ページ読込中...

ページ読込中...

[English]
| 溝川 貴司 [教授] |  |
|
| homepage | ||
| 専門分野 | 固体物理学・放射光分光 | |
| 研究テーマ・研究活動 | ||
| ○強相関電子系の電子状態 ○光電子分光・逆光電子分光 ○X線分光・散乱 ●日本物理学会 |
||
真空中で固体に真空紫外線やX線を照射すると表面から光電子が放出されます。この光電子の運動エネルギーと運動量を計測することにより、固体表面や固体中で電子が占有している状態を調べることができます(光電子分光)。逆に、電子線を固体表面に照射して放出される光子のエネルギーを測定することにより、電子に占有されていない状態の情報が得られます(逆光電子分光)。当研究室では、これらの電子分光に加えて、高輝度で波長可変な放射光を利用するX線分光・散乱を実験手段として、固体表面や固体中において電子の織り成す多彩な現象を、電子相関という切り口で研究しています。
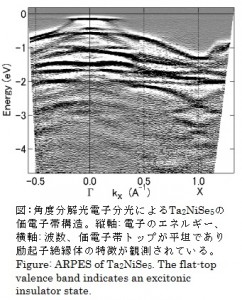 主な研究対象は、磁性や超伝導、金属絶縁体転移などの面白い物性を示す遷移金属化合物(d電子系)と希土類化合物(f電子系)です。dあるいはf電子系の電荷・スピン・軌道という自由度が格子振動と複雑に結合して、その多様な磁気的・電気的性質の発現を担っています。電子分光やX線分光による電子状態の計測結果に基づいて、物性のメカニズムを考察することができます。例えば、図のように角度分解光電子分光でバンド構造を観測し、電子間相互作用と電子格子相互作用を取り入れたモデル計算と比較することによって、電子相関や格子振動の効果を評価することができます。d電子系やf電子系は基礎物性の研究対象としての面白みだけでなく、光合成の活性中心のマンガンクラスターやリチウムイオン電池の正極のコバルト酸化物など、触媒やエネルギー変換材料としても重要です。電子分光・X線分光を駆使して表面・界面の複雑な電子状態の役割を解明することによって、従来材料の性能改善や新しい材料の開発に貢献することを目指しています。
主な研究対象は、磁性や超伝導、金属絶縁体転移などの面白い物性を示す遷移金属化合物(d電子系)と希土類化合物(f電子系)です。dあるいはf電子系の電荷・スピン・軌道という自由度が格子振動と複雑に結合して、その多様な磁気的・電気的性質の発現を担っています。電子分光やX線分光による電子状態の計測結果に基づいて、物性のメカニズムを考察することができます。例えば、図のように角度分解光電子分光でバンド構造を観測し、電子間相互作用と電子格子相互作用を取り入れたモデル計算と比較することによって、電子相関や格子振動の効果を評価することができます。d電子系やf電子系は基礎物性の研究対象としての面白みだけでなく、光合成の活性中心のマンガンクラスターやリチウムイオン電池の正極のコバルト酸化物など、触媒やエネルギー変換材料としても重要です。電子分光・X線分光を駆使して表面・界面の複雑な電子状態の役割を解明することによって、従来材料の性能改善や新しい材料の開発に貢献することを目指しています。
When a solid surface is irradiated by ultraviolet or x-ray light under vacuum, photoelectrons are emitted from the surface. By measuring the energy and momentum of the photoelectrons, we can study occupied states of the solid (photoemission spectroscopy). On the other hand, we can study unoccupied states of the solid by detecting ultraviolet or x-ray light emitted from the surface under electron beam irradiation (inverse-photoemission spectroscopy). Our research interests primarily focus on electron correlation effect in various electronic states of solids that can be observed by means of the photoemission and inverse-photoemission spectroscopy as well as x-ray spectroscopy/scattering with synchrotron radiation.
In particular, we are interested in transition-metal compounds (d-electron systems) and rare-earth compounds (f-electron systems) that show rich physical properties such as magnetism, superconductivity, and metal-insulator transition. The rich phenomena are derived from the spin, charge, and orbital degrees of freedom of the d– or f-electrons that are coupled with lattice in a complicated manner. We can study their mechanisms on the basis of the electronic structural information from the electron and x-ray spectroscopy experiments. For example, band dispersion can be probed by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy as shown in the Figure and can be analyzed by model calculations including electron-electron and electron-lattice interactions.
In addition to the interests in the fundamental electronic structures, useful catalysts and energy materials can be developed using d– and f-electron systems such as Mn clusters for photosynthesis and LixCoO2 cathode for Li-ion battery. By proving the complicated surface or interface electronic states with electron or x-ray spectroscopy, we aim to contribute to improvement or development of future energy materials.