専門分野
宇宙線物理学
宇宙線で天体物理現象と暗黒物質を研究する
研究テーマ
宇宙線とその発生源の観測と理論的研究
キーワード
宇宙線観測, CALET, 宇宙線加速, 宇宙線伝搬, 暗黒物質
LINKS
RESEARCH OVERVIEW
研究概要
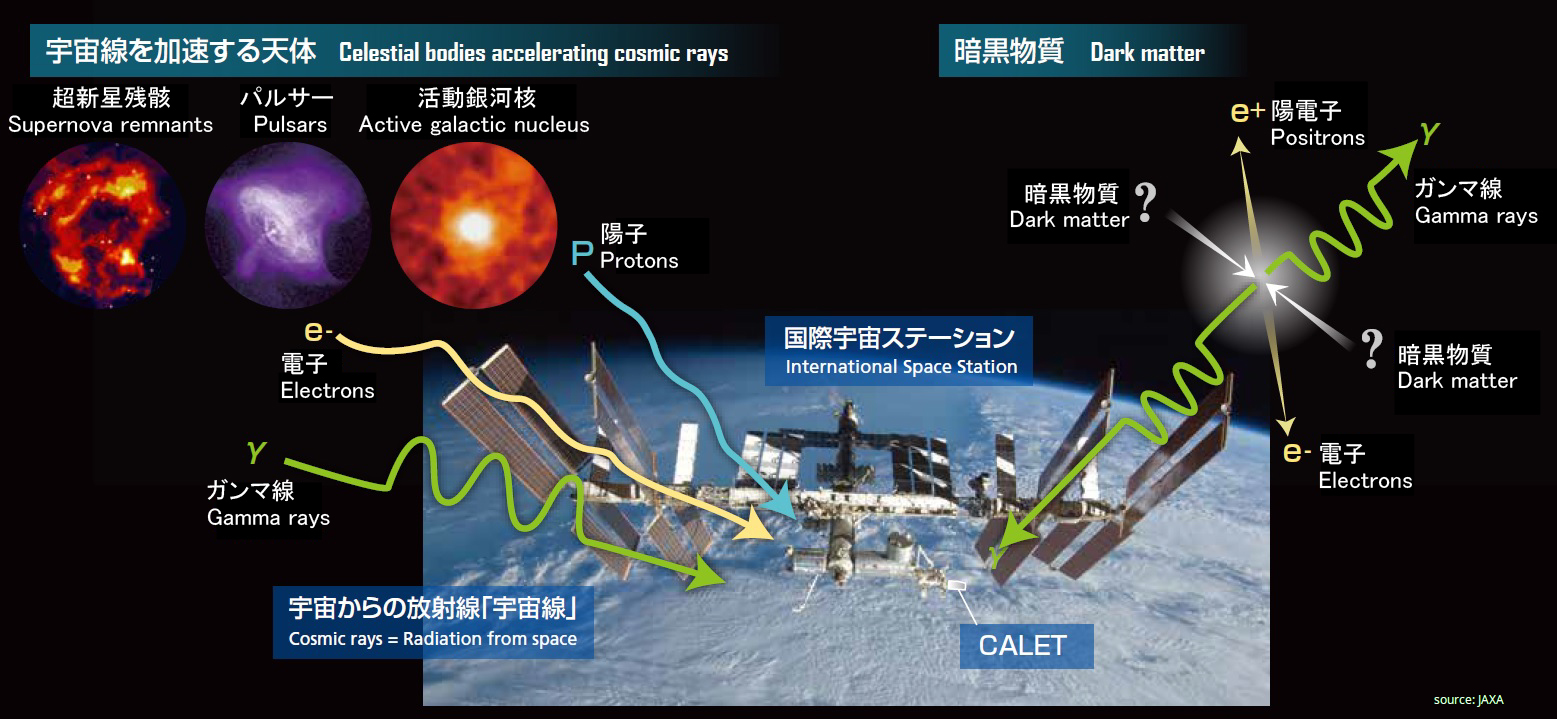
宇宙線は、宇宙空間で高い運動エネルギーを持つ粒子(原子核、素粒子)である。超新星残骸(SNR)やパルサーのような強い磁場を持つ天体によって加速されるほか、暗黒物質の消滅や崩壊でも生成される可能性があり、これらの現象を研究するためのメッセンジャーとなっている。宇宙線のエネルギー範囲は人工の粒子加速器の上限をはるかに超えるため、超高エネルギーでの物理過程を研究するための貴重なツールでもある。
荷電粒子である宇宙線は、その発生源から地球への旅の途中で銀河磁場によって偏向されるため、その到達方向は発生源の方向には戻らない。 磁場や星間物質との相互作用により、宇宙線はエネルギーを失い、エネルギースペクトルが変化し、二次宇宙線が生成される。したがって、宇宙線の起源と伝搬について一緒に研究する必要がある。 CALorimetric Electron Telescope(CALET)は、国際宇宙ステーション(ISS)に設置された宇宙線検出器で、2015年から稼働している。その主な目的は、TeVエネルギー領域までの電子・陽電子宇宙線のエネルギースペクトルを高精度で直接測定することである。
本研究室では、CALETデータの解析と観測結果の解釈に着目し、近傍のSNR宇宙線源や、暗黒物質の消滅・崩壊の兆候を探る。また、宇宙線の加速・伝搬モデルや暗黒物質候補粒子のモデルについても研究する。
MESSAGE to STUDENTS
学生へのメッセージ
宇宙を実験室として使いましょう! 宇宙線を観測することで、最も小さなスケールでの素粒子物理学を研究することができます。 宇宙において通常の物質よりもはるかに豊富であるダークマター(暗黒物質)は、素粒子物理学の標準模型以外の素粒子であると考えられています。ヒッグス粒子の発見に続き、この粒子の本質を解明することが次の大きな課題です。 宇宙線のエネルギースペクトルには、この素粒子の痕跡を見つける可能性があり、その探索を通じて、超新星残骸やパルサーなどの宇宙線の天体物理学的起源に関する興味深い情報を得ることもできます。
学歴・経歴
2006年 エルランゲン大学理学部 卒業
2011年 エルランゲン大学理学部 博士(理学)
2012年 東京大学宇宙線研究所 特任研究員
2013年 早稲田大学理工研究所 次席研究員
2014年 早稲田大学理工学術院国際教育センター 助教
2018年 早稲田大学理工学術院国際理工学センター 准教授
2023年 神奈川大学工学部 プロジェクト研究員
2023年 現職
所属学協会
- 日本物理学会
- ドイツ物理学会
Field of study
Cosmic-ray Physics
Study astrophysical phenomena and dark matter through cosmic rays
Research Themes
Observation and theoretical study of cosmic rays and their sources
Keywords
cosmic ray observation, CALET, cosmic ray acceleration, cosmic ray propagation, dark matter
RESEARCH OVERVIEW
Cosmic Rays are particles (nuclei, elementary particles) with high kinetic energy in space. They are accelerated by astrophysical objects with strong magnetic fields such as supernova remnants (SNR) and pulsars, and might also be created in the annihilation or decay of dark matter, which makes them a messenger for studying these phenomena. Since the energy range of cosmic rays far exceeds the upper limit of man-made particle accelerators, they are also a valuable tool to study physical processes at extreme energies.
Being charged particles, cosmic rays are deflected by the galactic magnetic field on their journey from their sources to Earth, so their arrival direction does not point back towards their source. In interaction with the magnetic field and interstellar medium, the cosmic rays also lose energy which modifies their energy spectrum and secondary cosmic rays are produced. Therefore, it is necessary to study the origin and propagation of cosmic rays together.
The CALorimetric Electron Telescope (CALET) is a cosmic-ray detector on the International Space Station (ISS), in operation since 2015. Its main objective is to directly measure the energy spectrum of electron and positron cosmic rays up into the TeV energy range with high precision.
This laboratory’s research focuses on the analysis of CALET data and interpretation of the observation results, aiming at finding signatures of nearby SNR cosmic-ray sources as well as of dark matter annihilation or decay. In this context, we also study models of cosmic ray acceleration and propagation as well as those of dark matter candidate particles.

MESSAGE to STUDENTS
Let’s use the Universe as our laboratory!
We can study elementary particle physics which is at the smallest scales by observing cosmic rays.
Dark Matter, which is known to be far more abundant than ordinary matter in our Universe is hypothesized to be a new elementary particle from beyond the Standard Model of particle physics. After the discovery of the Higgs boson, elucidating the nature of this particle is the next great challenge.
The energy spectra of cosmic rays may contain a signature of this elusive particle, and while searching for it we also can gain exciting information about the astrophysical sources of cosmic rays, such as supernova remnants and pulsars.
Education and Career
2006 University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Faculty of Science, Physics Diploma
2011 University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Faculty of Science, Doctor of Natural Sciences
2012 The University of Tokyo, Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, Project Researcher
2013 Waseda University, Research Institute for Science and Engineering, Junior Researcher
2014 Waseda University, International Center for Science and Engineering Programs, Assistant Professor
2018 Waseda University, Global Center for Science and Engineering, Associate Professor
2023 Kanagawa University, Faculty of Engineering, Project Researcher
2023 Current Position
Professional Memberships
- The Physical Society of Japan
- Deutsche Physikalische Gesellschaft

